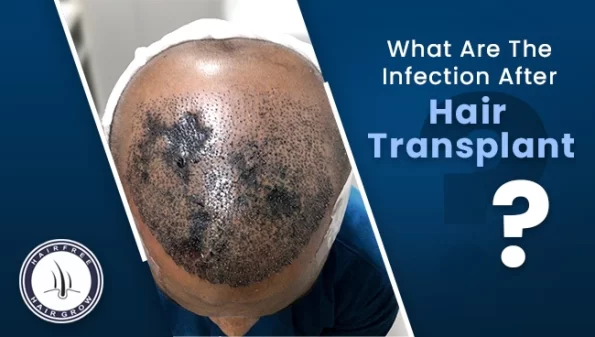
It seems like you’re looking for information about hair plug infection, which is a rare complication that can occur after a hair transplant. The symptoms of this infection include pain, discharge, discoloration of the skin, and fever. Fortunately, it is a rare complication, with less than 1% of patients experiencing it. Recognizing and preventing infection after hair transplant is crucial for successful results and a smooth recovery.
Hair loss is a common condition that affects many people, with up to 85% of men and 40% of women experiencing it. A hair transplant is a safe and effective procedure for treating hair loss, but it can sometimes result in complications such as infection.
During a hair transplant, the surgeon will numb the scalp and remove a portion of skin containing hair follicles from the donor area. They will then clean the area where the hairs will be transplanted and make tiny cuts in the receiving area. The hairs are then placed into these cuts, which are known as hair plugs.
If you experience symptoms of a hair plug infection, it’s important to seek medical attention right away. Antibiotics and other treatments can be used to help treat the infection. Additionally, there are other possible complications of hair transplant, including bleeding, scarring, and poor hair growth. Before the procedure, your surgeon will discuss these risks with you.
How Do You Know If You Have an Infection After Hair Transplant?
After a hair transplant, it is normal to experience slight discomfort and redness, but infections are rare. However, it is important to be cautious as hair transplants involve making incisions into the skin, which can increase the risk of infection.
If the hair transplant wounds become infected, symptoms may start to appear about 3-7 days after the surgery. These symptoms may include:
- Swelling
- Pus discharge
- Redness or discoloration
- Pain
- Itchiness
- Bleeding
If these symptoms persist or worsen after a few days, you may also experience fever, headaches, nausea, and vomiting. In such cases, contacting your doctor or hair transplant surgeon immediately is important to receive prompt medical attention.
What Can Cause Hair Transplant Infections?
Hair transplant infections can be caused by several factors, including improper hygiene, excessive scabbing, and underlying medical conditions. Following your surgeon’s instructions for caring for your hair after the procedure is essential, including washing your hair regularly and keeping your wounds clean.
You should also avoid touching your healing wounds with dirty hands, as this can transfer infection-causing microbes. Excessive crusting can also lead to infection, so it’s important not to scratch or itch the affected area.
Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as autoimmune diseases, HIV, high blood pressure, diabetes, cancer, and severe obesity, can make you more susceptible to wound infections.
Preventing Infection and Ensuring a Successful Recovery
1. Have Your Hair Transplant at a Licensed Clinic
Choose an experienced surgeon and a reputable clinic that follows strict hygiene rules to reduce the risk of infection. Check customer reviews before selecting a clinic.
2. Follow Pre and Post-Surgical Care Instructions
Your surgeon will provide instructions on what to do before and after the hair transplant. Follow them to minimize the risk of infection.
3. Avoid Scratching Your Scalp or Picking at Scabs
Your scalp will be itchy after the procedure, but avoid touching, rubbing, or scratching it. This can damage the new hair and introduce pathogens to the incisions on your scalp.
4. Avoid Vigorous Exercise
Strenuous exercise can make your scalp sweaty and itchy, increasing the temptation to scratch it. Avoid exercising until your surgeon advises otherwise.
5. Avoid Swimming
Do not swim in fresh or chlorinated water for 3 to 4 months after the transplant to prevent pathogens from entering the incisions on your scalp. Swimming can also dislodge the transplanted hair follicles.
6. Use a Saline Spray Solution
Apply a saline spray solution recommended by your surgeon to your scalp twice a day to remove dirt and prevent bacterial growth.
7. Avoid Alcohol, Smoking, and Tobacco Products During Recovery
Alcohol, smoking, and tobacco products can slow down the healing process and increase the risk of infection. Avoid them during recovery to help your body heal faster.
How Long Should it Take for My Hair Transplant to Heal?
After a hair transplant, the initial healing process usually takes around 5-7 days for the wounds to heal and for any swelling or redness to subside. However, it may take several months before the full results of the transplant are visible.
In some cases, the transplanted hair may fall out within two weeks after the procedure, but this is normal, and the hair should start to grow back within a few months. It typically takes 4-5 months to get a good idea of your new hair, and the full process can take up to 18 months. Following your surgeon’s post-operative care instructions is important to ensure proper healing and optimal results.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an infected hair transplant can be a serious and uncomfortable complication of this popular cosmetic procedure. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition and following the proper precautions and post-operative instructions can help prevent infection and ensure a successful recovery.
We hope that this article has been informative and helpful in providing you with the information you need to outrank the existing content on this topic. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to us.
Written By
MBBS, MD
Dr Pratibha Pradhan has a good experience in aesthetic Dermatology and is an expert in hair transplant field. She has wide experience in dealing with infections that may arise after hair transplant.
Disclaimer
We’ve made all possible efforts to ensure that the information provided here is accurate, up-to-date and complete, however, it should not be treated as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. See Detailed Disclaimers Here.